
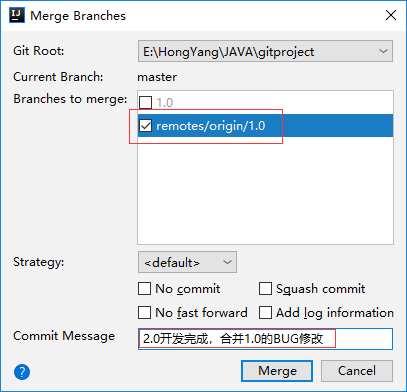
In this blog, we have seen how to add the existing code to the Azure Devops using command prompt. If everything went correctly we will see the message as above.Ĭommands which are used to add code to Repository If the Git is setup for the first time mean it will ask for credentials To get the Git Repository URL open the newly created repository and copy the URL.
Now run the below commands one after anotherĬmd: git commit -m "RELEVANT COMMIT MESSAGE" Now open a command prompt and locate your file location by giving cd > Once the Repository is created it will get selected by default. You can uncheck Add a README checkbox, Normally it will add a readme.txt file in the repository if it is checked. Cloning a repository from a remote server downloads the project to your local computer and leaves you with a local Git repository. Give Repository Name as per requirement, in my case I have given as "Test Repository". From the dropdown click on "New repository".Ī panel will appear in that Choose Repository type as Git. Open DevOps and choose the respective project.įrom Repos click on Files and click on the repositories which is already there, in my case it is "Internal". I) Create a Git repository in Azure DevOps
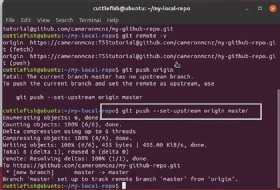
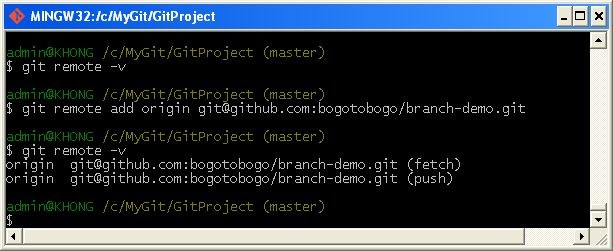
You can also see that both of the remote repositories have the same project name amazing-project and that gives us one reason why the remote repository names in the remote server and the shortnames in our local repositories should not be the same! In the above image you can see that I used the shortname friend to refer to my friend's remote repository. We can use the command git remote add in order to add a link to their remote repository in our local repository. And let's assume we want to be able to fetch code from their remote repository. Suppose we have a friend who forks our remote repository so they can help us on our project. I will answer that question with another example. So final question, why don't we just use the same name? In many cases you will have links to multiple remote repositories in your local repository and each of those will have a different shortname. And in our example above it is called origin.īasically origin is the default shortname that Git uses for a remote repository when you clone that remote repository. And this shortname kind of acts like an alias for the url, it's a way for us to avoid having to use that entire long url in order to push or fetch code. It is the shortname we are going to use whenever we want to push or fetch code from that remote repository. The other name that we have for our repository is the shortname that it has in our local repository that is related to the URL of the repository. And in our case that is 'amazing-project'. This can be kind of thought like a project name. Enter the following commands: Shell git init git add git commit -a -m Initial commit git remote add origin git. Well one of the names that we have for our repository is the name it has on GitHub or a remote server somewhere. So why does it seem like there are two names for the remote repository? Now, this may be a bit confusing because in GitHub (or the remote server) the project is called 'amazing-project'. Finally, i solved my issue, if you also fetch issue like i had then you can just follow bellow command and solve. There you will see that in order to push or fetch code from your remote repository you will use the shortname 'origin'. He know how can we resolve this issue so i remove my old remote and added new remote url on my existing repository. If you run the command git remote -v it will list all the remote repositories that are linked to your local repository. The remote repository and the local repository are linked. Then you would have something like what you can see in the diagram below:īecause you cloned the repository. Supposed you have a remote repository called amazing-project and then you clone that remote repository to your local machine so that you have a local repository. Therefore in order to properly answer this questions we need to understand what origin is. The rest of the links need to have different names. However only one of those links can be called origin. Alternatively, in Visual Studio, go to Repository Settings, and edit your remotes. In your Git client, run: git remote set-url 

 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
